Electromagnetic locks (or Maglocks) are very efficient, low-power locks with a range of accessories to suit most applications.
Their reliability, ease of installation, and compatibility with a wide range of security systems make them a popular choice among locksmiths and security professionals. This guide will provide an overview of electromagnetic locks, their working principles, and types.
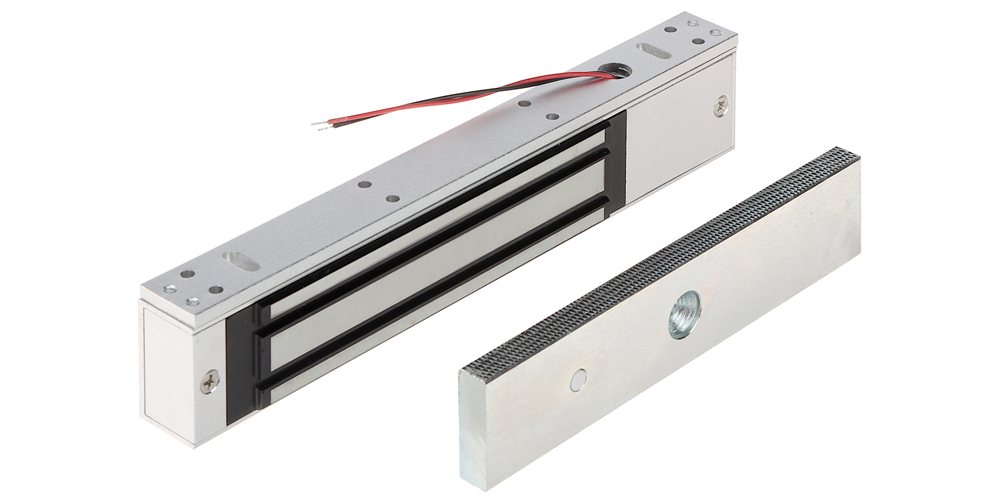
Electromagnetic locks are locking devices that use magnetic force to secure doors. They consist of two primary components:
Electro-magnetic locks are key components in modern access control systems. They have no moving parts making them more reliable and requiring less maintenance.
The armature and electromagnet, when energised, hold a door securely fastened by creating a powerful magnetic field. When the power is cut the armature is released, thus giving access or exit through the doorway.
Key points:
Electromagnetic locks come in various types to suit different applications:
Single Door Maglocks: These are the most common type and are used for single doors. They are available in different holding forces, typically ranging from 600 lbf to 1,200 lbf.
Double Door Maglocks: Designed for double doors, these locks feature two electromagnets and two armature plates, providing secure locking for both doors simultaneously.
Shear Locks: A specialized type of electromagnetic lock, shear locks are designed to offer higher security by providing a shearing force between the magnet and armature plate, which prevents lateral movement.
Mini Maglocks: Smaller versions of standard maglocks, mini maglocks are ideal for applications where space is limited, such as cabinets or smaller doors.
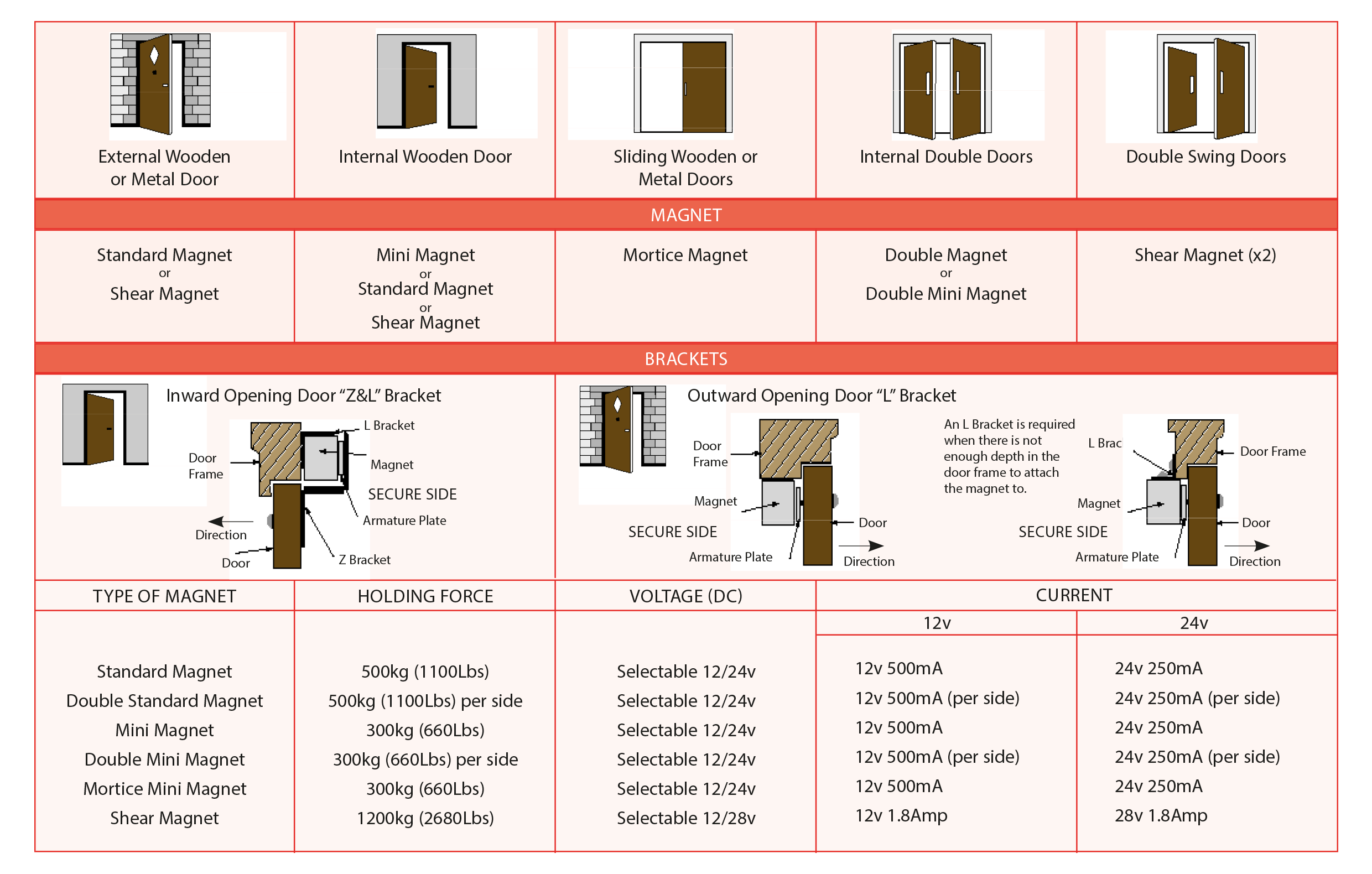
If you need any help specifying a magnetic lock, please do not hesitate to call us on 0131 555 0909 or email sales@keyprint.co.uk.
.................................................................................................................
45 Assembly Street
Edinburgh
EH6 7BQ
Keyprint Security Ltd. is a trade only supplier.
All prices exclude VAT and are subject to change without notice. E.&O.E.
Copyright © 2025 Keyprint Security. All rights reserved.


